The Tax Preparer’s Ultimate Guide to Data Security
In 2021, cybercrime cost U.S. businesses nearly $7 billion, yet 29% of CEOs and 40% of chief security officers admitted that their organizations remain unprepared for a large-scale cyberattack.
You can immediately institute many things to help keep data secure, such as getting up to speed on the most prevalent threats. Criminals continue to change their method of operation, and if you don’t stay up to date on the latest threats, you won’t be able to implement the appropriate measures to stop them.
What is Data Security?
Data security is a vague term often confused with similar terms such as data protection and privacy. Though all three are required to protect against threats, there are significant differences between them.
First, data security is used to protect data from unauthorized access, theft, or corruption in all its stages, including:
- Data creation
- Data sharing
- Data storday
- Data Deletion
- Data usage
Data security includes putting protocols in place to secure server data, appropriately limiting administrative access to data to those that require it, and implementing policies for securely deleting data. Data security measures include encryption, masking, and redacting when appropriate. This protects against external theft and keeps an organization’s data secure internally.
Data security and data protection are often confused since the two sound similar. But data security is used to keep your data safe from unauthorized access, whether from cyberattacks originating outside or data breaches from within the organization. In contrast, data protection safeguards your current data should it be compromised or lost.
For instance, data security is used to protect data from cyber attacks, while data protection is used to keep your data safe and easily replicable should a cyber attack occur.
Finally, data privacy is another important concept. While keeping data private is also a concern with data security, data privacy most commonly refers to ensuring the proper use of all personal data. This is done in various ways, including:
- Allowing clients to unsubscribe from email notifications
- Requiring client consent before sharing data such as an email address, home address, or phone number
- Using proper data security measures to protect customer data from breaches and cyber attacks
- Keeping purchasing details confidential.
Why Data Security Is Vital for Tax Professionals
With the level of information shared between tax professionals and their clients, it’s no wonder that tax preparation firms are a popular target for cybercriminals. As a tax professional, keeping your client’s data secure is your responsibility. A data breach, even a small one, can expose your client’s personal information to cybercriminals while exposing your firm to possible lawsuits and even bankruptcy. Not to mention, these breaches can put you in violation of various federal and state laws designed to keep client data safe. If you’re ready to get serious about security, the following measures can help.

Guard Your Businesses Confidential Data
When instituting data security, remember it’s important to secure both company and client data since information such as employee contact details, Social Security numbers, and banking information are also valuable to cybercriminals.
When securing your network, remember that not all threats come from outside an organization. While most data breaches originate from an unknown source, the possibility of a data breach within the company cannot be discounted. While safety measures typically address outside threats, internally securing data needs to be part of your data security process.
Protect Your Clients’ Personal Information
With document sharing so prevalent in the tax preparation business, it’s essential to offer a secure portal where documents can be safely shared between clients and your business. Instituting security measures such as two-factor authentication and offering secure messaging and emailing options can also help reassure clients that their data is safe.
Safeguard Your Brand’s Reputation
Exposing your client’s personal information to hackers and other cyber criminals isn’t only catastrophic for them- it’s also one of the fastest ways to destroy your reputation. When clients share their confidential data, they trust you to protect it. When even a minor data breach occurs, that trust is destroyed, and your clients are likely to find another tax preparer that will keep their documents safe.
Bad publicity can also prohibit you from attracting and retaining good employees and can even make it difficult to secure a loan or financing for your business.
Types of Data Breaches
To better protect your business from data breaches, you’ll first need to understand the types of threats facing your business daily.
Cyber Attacks
A cyber attack occurs when a criminal tries to gain unauthorized access to electronic data. Whether it’s a desktop computer or a network system housing data for thousands of businesses, a cyber attack can inflict untold financial and reputational damage.
Even with protections in place, cybercriminals use sophisticated tactics to gain access to your system and data. Ransomware, phishing, and malware are some of the more common cyber attacks, which we’ll discuss next, but you should be aware of other types of cyber attacks.


Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
This occurs when a breach in security allows a cybercriminal to eavesdrop on a transaction between two parties, positioning themselves between the two communicating parties to intercept or change a message. Without a secure network for communicating with your clients, you’re vulnerable to MITM attacks.

Password Attack
This can come from within the organization itself, or from the outside, with hackers having sophisticated tools at their disposal to help guess your password. They can also access personal data about an individual and use that information to guess a password, which is why having a complicated password works best.

Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack

URL Interpretation
A URL interpretation attack can be particularly damaging to a tax preparation business. A cybercriminal can redirect the URL to gain access to administrator privileges, where they can manipulate or steal data.

Insider Attacks
Not all cybercrime is committed by unknown assailants. You can also leave yourself vulnerable to in-house attacks simply because of your employees’ proximity to information such as passwords and client files. The best way to protect against in-house attacks is to limit employee access to specific data.
Try Proclient
Free

Ransomware
Ransomware attacks have increased by 42% in the first half of 2022. Attackers use ransomware malware to encrypt your files, preventing you from accessing them. Once you’re locked out, the attackers demand money or “ransom” to restore access to your data. As ransomware attacks have increased, attackers have resorted to threats such as releasing data to the public to convince reluctant companies to pay up. A ransomware attack during the tax preparation season can severely disable or even destroy a tax preparation business.
Phishing
Phishing involves criminals sending email or text messages with a link or attachment in an attempt to steal passwords gain access to personal or confidential data, or gain access to your bank account. Phishing is also used to download malware onto your computer.
Early on, it was easy to recognize a phishing attempt, but with cybercriminals using more sophisticated tools, emails and texts often look credible. Many phishing attempts are designed to look like they’re coming from your bank, a utility company, or a popular online shopping site. They draw you in with claims of problems with your account, or that suspicious activity has been noted. All you have to do to fix the problem is to click on the link or download the attachment. If you click on the link, the scammers immediately gain access to your data.
To protect your company against phishing, all employees should be trained in how to recognize phishing attempts before responding to an email or text.


Malware and Viruses
The terms malware and viruses are often used interchangeably, but the two differ. While a virus is a form of malware, you should be aware of other types of malware. Today, more than a quarter of all data breaches involve malware, which is used to steal or manipulate data and can take many forms, including spyware, viruses, trojan horse, and worms, and are usually distributed via an email attachment. However, pop-ups can also contain a virus.
Most Common Security Mistakes and How to Prevent Them
Perhaps the biggest mistake that businesses make is not taking cyber threats seriously, leaving their business vulnerable to attacks.
Everyone that maintains an online presence must institute the appropriate security measures to protect business and client data, including the following:

Password Security and Two-Factor Authentication
Password security is an area that is easy to beef up, yet many companies fail to enforce it. By instituting a robust password policy, you’ll prohibit employees from using common passwords such as 12345 or their birthday. Adding two-factor authentication to the mix is just smart business.
When using two-factor authentication, you require your employees and clients to use a second method to verify identities, such as entering a code sent via text or email. While not foolproof, requiring two-factor authentication can discourage hackers from looking for an easy target.
Data Encryption
Another way to safeguard data is to encrypt it. Data encryption translates data into another language, with only authorized individuals able to read it using an encryption key. A popular and effective security measure, encrypting, protects data when stored or in transit, such as an email. If you’re regularly sharing data with clients, make sure the data is encrypted.
Data Masking
Data masking is a technique that hides or scrambles data to produce an inauthentic copy. For tax preparers, it’s a good idea to use data masking on any document that contains sensitive information, such as Social Security numbers or credit card numbers. This is especially important when sharing client data with staff members to create a client mailing list or other marketing materials.
Access Management
One of the best preventive measures you can institute is proper staff training. Training should include how to create a strong password, how to recognize suspicious emails or texts, along with detailed instructions on how to handle any suspicious correspondence. Another area within your control is access levels. System access levels should be determined by the employee, with each employee receiving the appropriate level of access to do their job, but nothing more. And for businesses still dealing with paper documents, ensure they’re properly stored in a secure location.
It’s not only current employees you need to think about. Are you regularly removing any former employees from system access? If you’re not, it could come back to haunt you.
Ensure Your Business Tools Are Secure
- Making sure to back up all data
- Using extra precautions when working in a public area
- Never leaving confidential documents in public areas
- Never leaving your computer unattended
- Always using a secure Wi-Fi network
- Disposing of data properly, whether it’s paper documents or electronic
Try Proclient
Free

Secure Document Management is Critical for Tax Professionals
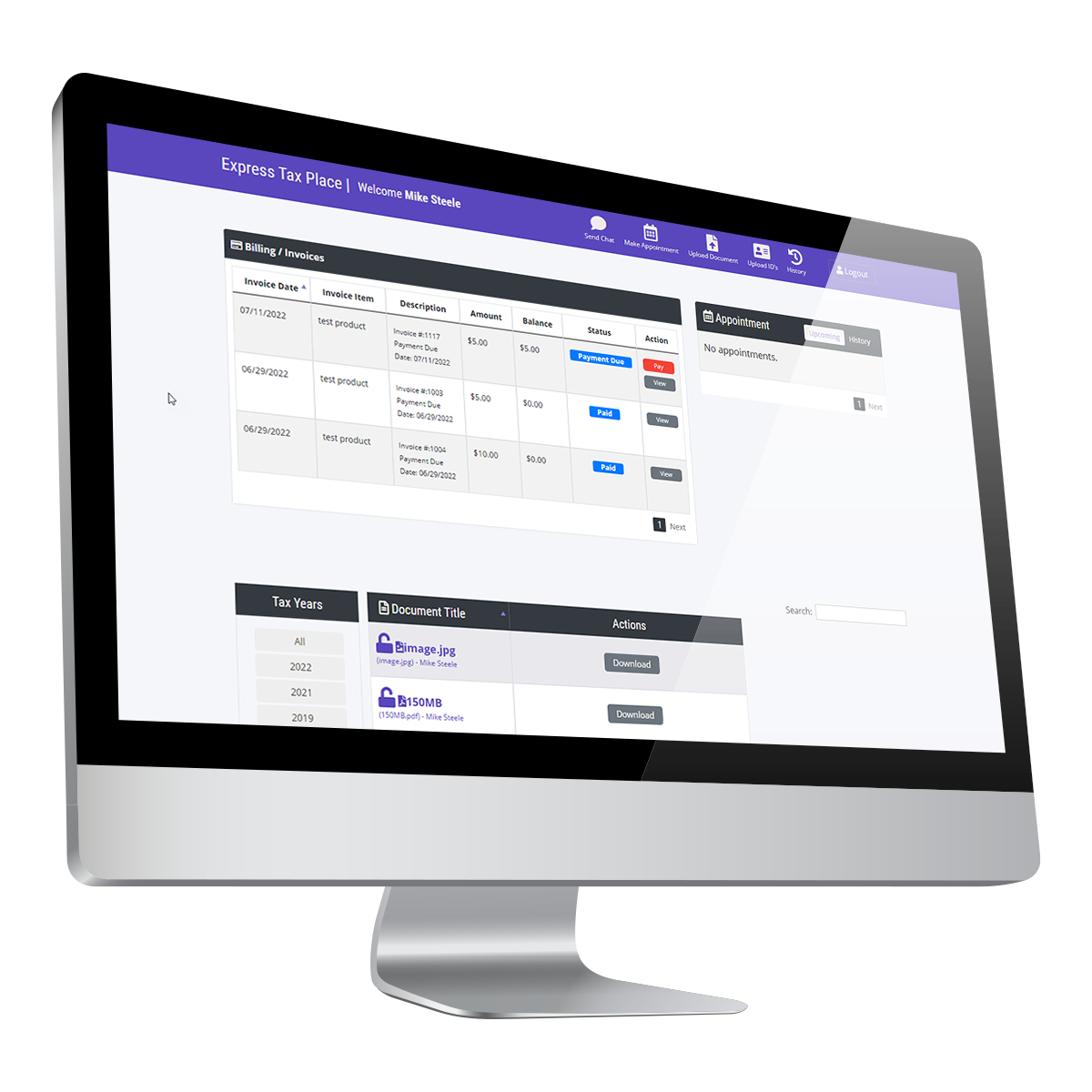
As a tax preparation firm, the most valuable commodity you have is your clients. When accepting a client, you’re given access to a lot of confidential data that can be easily exploited. It’s your responsibility to keep their data safe and out of the hands of those who would use it for their gains, be it a cybercriminal or a disgruntled former employee. Luckily, you don’t have to sacrifice convenience with security. With tools like ProClient, you can organize your office while ensuring that all client data remains safe and secure.
ProClient: Scheduling and Data Security All-in-One System
ProClient is an all-in-one system that offers convenient appointment scheduling, document management, invoicing, and a client portal. But along with streamlining administrative tasks, you’ll also get a system designed to protect confidential data.
Included in ProClient’s system are some top-notch security features, including the following:

Physical server security
PCI DSS Security
Automatic Encryption
SSL Protection
With ProClient, you can have an affordable, comprehensive application that keeps your data safe.
Learn more about protecting confidential data with ProClient by signing up for a free trial today.
Try ProClient Free
If you are sick and tired of using what feels like a million business tools, it’s time to try our comprehensive management system.
